The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) is a seven-step process designed to help organizations manage cybersecurity and privacy risks effectively. For small businesses entering federal contracting, RMF is not just a compliance requirement but a practical tool to protect sensitive data and compete in the federal marketplace. Recognizing the unique challenges small businesses face, NIST introduced the "Small Enterprise Quick Start Guide" (SP 1314) in July 2024, offering simplified guidance tailored for resource-limited organizations.
Key Takeaways:
- Why It Matters: RMF ensures compliance with federal cybersecurity standards, like FISMA, and strengthens security measures to protect data.
- Seven Steps: Prepare, Categorize, Select, Implement, Assess, Authorize, Monitor – each step builds a continuous cycle of risk management.
- Small Business Support: Resources like SP 1314 and tools from NIST make RMF accessible, even for businesses with limited budgets.
- Federal Opportunities: RMF compliance opens doors to lucrative federal contracts, especially for businesses handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
By following RMF, small businesses can build secure systems, manage risks effectively, and position themselves as reliable federal contractors. Ready to dive into the details? Let’s explore each step and how to make RMF work for your business.
Understanding the NIST Risk Management Framework RMF | Exclusive Lesson
The 7 Steps of the NIST RMF Process
NIST RMF 7-Step Risk Management Framework Process for Small Businesses
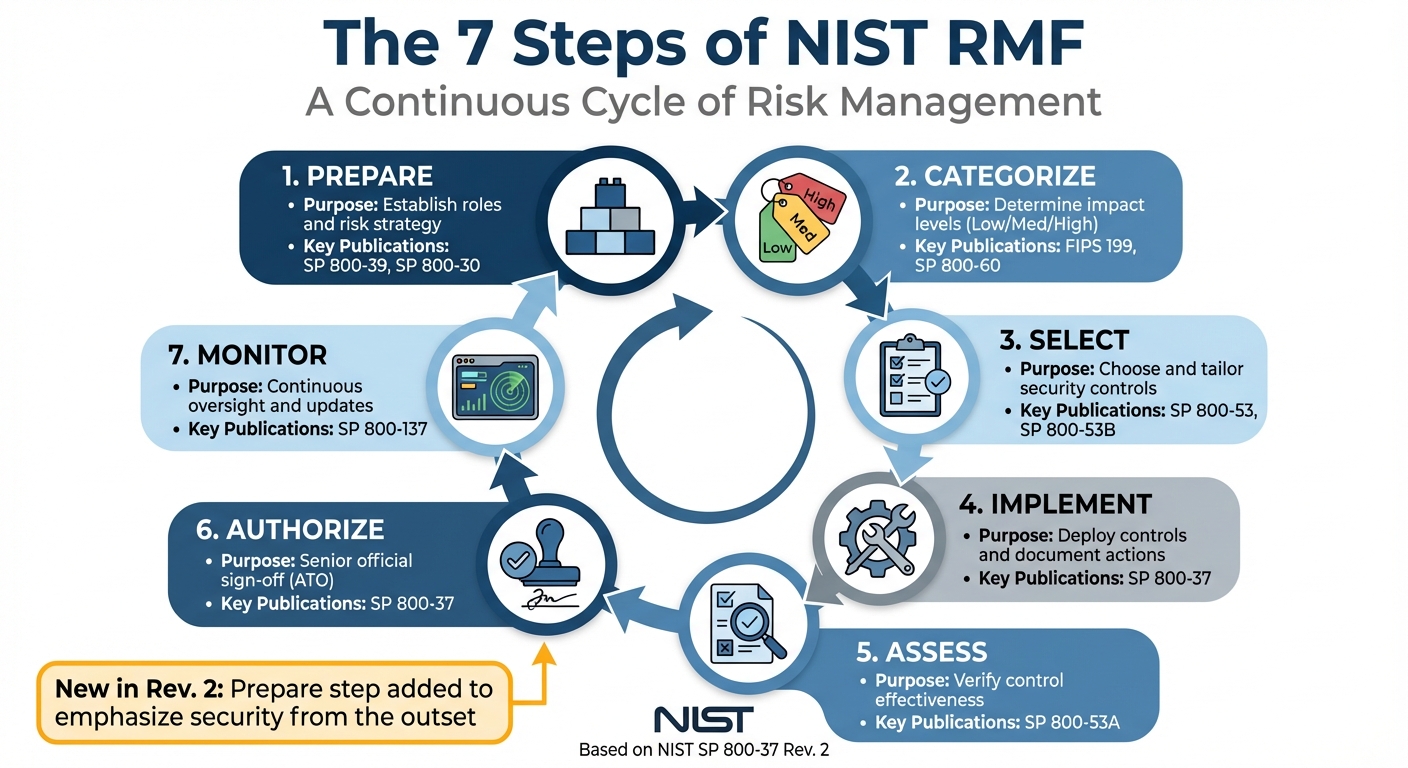
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) consists of seven sequential steps designed to create a thorough security and privacy program. Each step builds on the last, forming a continuous cycle of risk management that aligns seamlessly with your system development lifecycle.
Initially, the framework had six steps, but with the release of NIST SP 800-37 Rev. 2, a new step – Prepare – was added to emphasize integrating security measures from the outset. Art Clomera, Vice President of Operations at IPKeys, highlights the importance of this addition:
"The first step [Prepare] forms the solid foundation upon which the final security ‘structure’ will stand."
Here’s a quick overview of the seven steps:
| RMF Step | Purpose | Key NIST Supporting Publication |
|---|---|---|
| Prepare | Establish roles and risk strategy | SP 800-39, SP 800-30 |
| Categorize | Determine impact levels (Low/Med/High) | FIPS 199, SP 800-60 |
| Select | Choose and tailor security controls | SP 800-53, SP 800-53B |
| Implement | Deploy controls and document actions | SP 800-37 |
| Assess | Verify control effectiveness | SP 800-53A |
| Authorize | Senior official sign-off (ATO) | SP 800-37 |
| Monitor | Continuous oversight and updates | SP 800-137 |
Below, we’ll dive into each step, offering practical guidance for small businesses looking to integrate the RMF into their operations.
Step 1: Prepare
The Prepare step lays the groundwork for everything else. This is where you define risk management roles, establish your organization’s risk strategy, and identify risk tolerance levels.
For small businesses entering federal contracting, it’s crucial to assign specific individuals to cybersecurity roles instead of assuming "someone" will handle it. The RMF Quick Start Guide for Roles and Responsibilities can help even small teams map out duties effectively.
Another key part of this step is identifying "common controls" – shared security measures that apply across multiple systems. For instance, if you’re using a cloud provider, you can often inherit their physical security controls, which reduces your compliance workload.
To structure this step, refer to NIST SP 800-30 for conducting risk assessments and SP 800-39 for creating your overarching risk management strategy. These resources offer repeatable methods that small businesses can implement without needing expensive consultants.
Step 2: Categorize
Next, you’ll categorize your information systems based on their impact levels – Low, Moderate, or High – on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
This categorization determines the intensity of security measures your system will require. Many small businesses use the "high-water-mark approach": if one category (e.g., confidentiality) is rated High, the entire system is classified as High. For example, if your system handles sensitive federal data where integrity is critical, but confidentiality and availability are less critical, the system would still be categorized as High overall.
To guide this process, use FIPS 199 and NIST SP 800-60, which provide detailed instructions for conducting impact analyses. The results from this step directly influence the security controls you’ll select in the next phase.
Step 3: Select
With your system categorized, the next step is to select and tailor security controls from NIST SP 800-53, which lists over 1,000 security controls.
For small businesses, the key is to be strategic. More controls don’t always mean better security. Instead, focus on selecting controls that address real risks without disrupting your operations. Start by choosing a baseline of controls that matches your system’s impact level (Low, Moderate, or High) using NIST SP 800-53B. Then, customize these controls based on your specific business needs.
It’s also important to differentiate between "common controls" (inherited from external providers, like cloud services) and "system-specific controls" (unique to your system). This distinction helps avoid duplicating efforts and wasting resources.
Step 4: Implement
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. During the Implement step, you’ll deploy the selected controls and document every action. This might involve installing hardware, updating software, providing staff training, or revising policies.
Small businesses can use templates from NIST SP 800-37 to ensure consistent documentation. NIST also offers free tools, such as the Privacy Risk Assessment Methodology (PRAM) and RMF Online Introductory Courses, to help reduce costs. Additionally, the Small Enterprise Quick Start Guide (SP 1314) – released in July 2024 – provides tailored guidance for small organizations.
As Zoe Lindsey, Security Strategist at Blumira, points out:
"NIST’s RMF acknowledges that perfection isn’t necessary out of the gate – what matters is making progress and continually improving."
For small businesses, starting with your most critical assets and gradually expanding your framework is a practical approach. This is especially important given that nearly 80% of ransomware attacks in the first half of 2023 targeted small and mid-sized businesses.
Steps 5-7: Assess, Authorize, and Monitor
The final three steps ensure your system remains secure through continuous evaluation and improvement.
- Step 5 (Assess): This step involves verifying that your controls are working as intended. Use independent assessors or automated tools to evaluate effectiveness. NIST SP 800-53A provides detailed assessment procedures, and automation can streamline this process by increasing accuracy and reducing manual work.
- Step 6 (Authorize): A senior official, often your highest-ranking executive, reviews the assessment results and grants an Authorization to Operate (ATO). This formal approval confirms that the organization accepts any remaining risks.
- Step 7 (Monitor): This step shifts your focus to continuous monitoring. Regularly track control performance, watch for new threats, and reassess risks as your environment changes. NIST SP 800-137 offers guidance on setting up a monitoring program. For federal contractors, this ongoing oversight is critical to maintaining compliance over time.
Monitoring ensures that security isn’t treated as a one-time task. Changes to your systems, evolving threats, or updates to federal requirements will all feed back into the RMF cycle, keeping your organization prepared for what’s next.
Benefits of NIST RMF for Small Businesses
Adopting the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) offers small businesses more than just compliance – it provides a structured way to handle cybersecurity risks while opening doors to federal contracting opportunities.
Strengthened Security and Risk Management
The RMF gives small businesses a practical, systematic approach to protecting their data and systems, even with limited resources. Unlike one-size-fits-all checklists, the framework emphasizes continuous, near real-time risk management, which helps detect threats early.
One standout benefit is its ability to guide cost-effective decision-making. With RMF, business leaders can focus their limited budgets on addressing the most critical threats.
The framework also ensures accountability by assigning specific roles for managing controls and risk-related tasks. This level of clarity is particularly helpful for small teams where employees often juggle multiple responsibilities.
By tackling security and privacy risks early in the system development life cycle, businesses can build a strong foundation to withstand cyber threats and recover quickly from incidents. RMF’s structure promotes proactive risk management, assigning clear responsibilities that enhance both security and overall resilience.
Another key advantage is its integrated approach. RMF ties system-level security initiatives to broader organizational risk management, streamlining the handling of cybersecurity, privacy, and supply chain risks. This unified process simplifies what could otherwise be a complex set of challenges.
These improved security measures don’t just protect your business – they also give you a competitive edge, especially when pursuing federal contracts.
Expanded Federal Contracting Opportunities
For small businesses, RMF compliance is often a gateway to securing federal contracts. The framework supports the risk management programs required under the Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA), which governs federal information systems. Without RMF compliance, many of these opportunities remain inaccessible.
A critical part of RMF is the "Authorize" step, where a senior official grants formal Authorization to Operate (ATO). This step reassures federal agencies that proper security measures are in place and that any remaining risks have been formally accepted.
Implementing RMF also helps businesses meet the requirements of NIST SP 800-171, which focuses on protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Compliance with this standard is often mandatory for Department of Defense and other federal contracts.
Perhaps most importantly, RMF demonstrates that security is embedded into the system development life cycle from the beginning. This proactive approach signals to federal procurement officials that your business prioritizes risk management.
How to Implement NIST RMF: Practical Tips
Using NIST SP 800-37 and SP 800-53 as Guides
To successfully implement the Risk Management Framework (RMF), you’ll need two key documents: NIST SP 800-37 and SP 800-53. Think of SP 800-37 as your roadmap – it lays out the seven-step RMF process. SP 800-53, on the other hand, is your toolbox, offering a catalog of security and privacy controls to use during the "Select" step.
For small organizations, starting with NIST SP 1314, the Small Enterprise Quick Start Guide (July 2024), can make the process more manageable. According to NIST:
"This guide is designed to help small, under-resourced entities understand the value and core components of the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) and provide a starting point for designing and implementing an information security and privacy risk management program."
Leverage the Quick Start Guides to tackle each RMF phase one at a time. As you move forward, consult more specialized publications for detailed guidance. For example, when you reach the "Implement" step, you might refer to SP 800-34 for contingency planning, SP 800-61 for incident handling, or SP 800-128 for configuration management.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Implementing RMF can feel overwhelming, especially for small businesses with limited resources. But there are practical strategies to help you integrate RMF effectively without overextending your team.
One common challenge is navigating the extensive RMF documentation while juggling minimal cybersecurity resources. To ease the burden, avoid trying to implement everything at once. Instead, focus on common controls – these are controls that multiple systems in your organization can share. This approach simplifies accountability and eliminates the need to create unique controls for every system.
Another tip: integrate security and privacy considerations into your System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) from the start. Doing this early can save time and money while ensuring your security and privacy plans align with your actual implementations.
For additional support, check out the NIST Small Business Cybersecurity Corner, which offers primers on standards like SP 800-171 for protecting Controlled Unclassified Information. NIST regularly updates its Quick Start Guides to address evolving threats, with the most recent updates released on November 21, 2025.
The RMF is designed with flexibility in mind, allowing you to scale tasks based on your organization’s unique risk levels and mission requirements. By starting small and focusing on what’s essential, you can steadily build a robust security and privacy program.
How GSA Focus Supports RMF Implementation
When it comes to navigating RMF implementation, meeting compliance standards and breaking into the federal market are key priorities. Here’s how GSA Focus helps make that process smoother.
How GSA Focus Simplifies Compliance
Balancing the demands of the NIST RMF and GSA Schedule requirements can feel overwhelming. That’s where GSA Focus steps in. Specializing in small business support, they offer comprehensive services for securing and managing GSA Schedule Contracts – a crucial step for entering the federal marketplace.
Since 2006, GSA Focus has been helping small businesses cut through the complexities of federal contracting. From document preparation to compliance assurance and negotiation support, their team handles the heavy lifting. Their "done-for-you" approach means you don’t have to become an expert in federal procurement rules while also focusing on your RMF program. Instead, you can concentrate on implementing the security and privacy controls your systems need while they take care of the administrative side of GSA Schedule compliance.
With a 98% success rate in securing GSA contracts and a refund guarantee, GSA Focus has built a strong track record. Their secure online portal simplifies document uploads, reducing approval delays and keeping the process efficient.
This hands-on support makes compliance less of a hurdle and more of a gateway to federal market opportunities.
Accessing Federal Market Opportunities
Once your RMF implementation is in place and your cybersecurity measures align with federal standards, the next step is making yourself visible to federal buyers. GSA Focus helps bridge that gap, cutting down the time and effort needed to access federal contracts.
The GSA Multiple Award Schedule (MAS) connects businesses to over 7.5 million IT products and services from more than 4,600 pre-vetted vendors. Earning a spot on this schedule can open doors to agencies actively seeking contractors familiar with frameworks like NIST RMF. GSA Focus provides end-to-end support, from securing your initial contract to managing ongoing compliance and reporting.
For small businesses handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) or pursuing contracts requiring an Authorization to Operate (ATO), aligning your RMF efforts with GSA Schedule requirements is crucial. GSA Focus offers advisory services to help you meet federal expectations for security controls and documentation, turning your RMF compliance into a competitive edge when bidding on contracts.
Conclusion
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) is far more than a box to check for compliance – it sets the benchmark for fulfilling FISMA mandates. For small businesses aiming to secure federal contracts, especially those that involve handling Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), adopting the RMF lays the groundwork for Authorization to Operate (ATO) decisions. It also positions your business as a trusted partner for federal agencies actively seeking contractors with strong security measures in place. This structured approach simplifies risk acceptance and streamlines the federal contracting process.
"Managing organizational risk is paramount to effective information security and privacy programs; the RMF approach can be applied to new and legacy systems, any type of system or technology… and within any type of organization regardless of size or sector." – NIST
One standout benefit of the RMF is the concept of reciprocity. If your business achieves authorization with one federal agency, that approval can often be leveraged across multiple contracts, saving both time and resources.
For small businesses with limited resources, tools like the SP 1314 Small Enterprise Quick Start Guide provide a practical roadmap for navigating the RMF. Additionally, the updated NIST SP 800-171 Revision 3 Small Business Primer (set to release on November 21, 2025) offers tailored guidance to help smaller organizations adapt security practices to their scale.
To make this process even more accessible, GSA Focus connects RMF implementation with opportunities in the federal market. Their experienced guidance simplifies compliance, allowing you to focus on safeguarding your systems. For small businesses, this partnership transforms RMF compliance from a daunting challenge into a competitive advantage, helping you meet both security standards and GSA Schedule requirements with ease.
FAQs
What is the role of the NIST RMF for small businesses?
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) offers small businesses a step-by-step method to pinpoint, evaluate, and address cybersecurity and privacy risks. This framework is specifically tailored to help protect sensitive data while ensuring businesses meet federal security guidelines.
For small businesses, adopting the NIST RMF means strengthening their security measures, fostering trust with federal clients, and staying compliant with government standards – key factors for thriving in the federal contracting space.
How can small businesses adopt the NIST RMF with limited resources?
Small businesses can embrace the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF) by leveraging its adaptable and scalable elements. Begin by pinpointing your most critical assets and customizing security controls to fit your unique operations. This approach minimizes unnecessary complexity and ensures your resources are directed toward what matters most.
For greater efficiency, focus on a risk-based strategy. Address the most pressing vulnerabilities and threats instead of attempting to tackle every possible risk. Tools like automation and continuous monitoring can streamline your efforts, allowing for real-time risk assessments and responses without overburdening your team or resources.
By aligning with NIST’s recommendations, small businesses can create a practical and effective cybersecurity program that matches their capabilities while strengthening their position in federal contracting opportunities.
What are the advantages of achieving RMF compliance for small businesses in federal contracting?
Achieving RMF compliance brings notable benefits for small businesses aiming to secure federal contracts. First and foremost, it bolsters your company’s cybersecurity defenses, ensuring that risks are managed continuously and sensitive data remains protected.
Beyond security, meeting RMF standards signals to federal agencies that your business is equipped to handle cybersecurity and privacy challenges effectively. This not only enhances your reputation but also gives you a competitive advantage in the federal contracting space, where such readiness is increasingly essential.
Related Blog Posts
- Regulatory Requirements for Federal Contracts
- GSA Cybersecurity Policies Overview
- How Policy Changes Affect Small Business Contracts
- Future of Federal Cybersecurity Contracts


