Federal buyers follow a structured process to select vendors for government contracts. This process prioritizes compliance with strict regulations, value for taxpayers, and fair competition. To succeed, businesses must meet mandatory requirements, such as registering on SAM.gov, maintaining certifications, and adhering to federal acquisition standards. Proposals are then evaluated based on technical quality, past performance, and pricing.
Key takeaways:
- Mandatory Requirements: Vendors must register on SAM.gov, obtain a Unique Entity ID (UEI), and meet responsibility standards. Some contracts require a GSA Schedule.
- Evaluation Criteria: Proposals are scored on technical capability, past performance, and cost. Non-compliance or incomplete submissions often lead to disqualification.
- Selection Methods: Contracts are awarded through either Lowest Price Technically Acceptable (LPTA) or Best Value Trade-Off, with the latter allowing higher-priced bids if they provide added benefits.
- GSA Schedule Benefits: Holding a GSA Schedule contract simplifies access to federal opportunities and signals credibility, but the process involves rigorous compliance and pricing strategies.
To improve your chances, ensure full compliance, offer competitive pricing, and highlight a strong track record. Partnering with experts can simplify the process and help secure federal contracts.
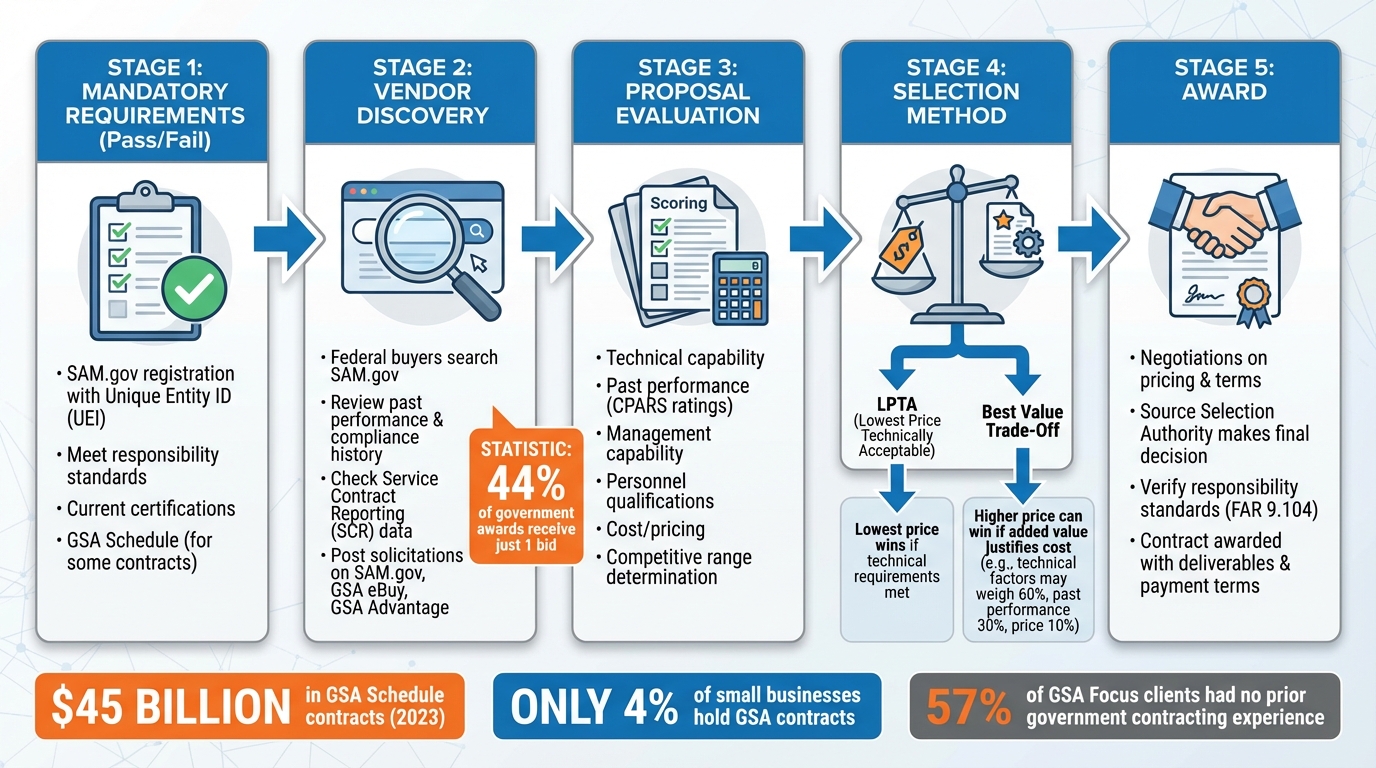
Federal Vendor Selection Process: From Registration to Contract Award
Understanding the Government Procurement Process
How Federal Buyers Set Evaluation Criteria
Before federal agencies solicit proposals, they establish clear evaluation standards to guide their selection process. These standards are split into two key categories: mandatory requirements, which vendors must meet to qualify, and scored criteria, used to identify the proposal that delivers the best value. This structured approach ensures that only qualified and cost-effective proposals are considered.
Mandatory Requirements: Pass-or-Fail Benchmarks
Federal buyers impose non-negotiable requirements that every vendor must meet. For starters, all vendors must register on SAM.gov and secure a Unique Entity ID (UEI). Additionally, vendors must prove they meet responsibility standards, are free of government exclusion lists, and maintain current representations and certifications.
In some cases, agencies require vendors to hold a GSA Multiple Award Schedule (MAS) contract. While this opens doors to lucrative opportunities, the process to obtain a MAS contract is rigorous and often deters participation. Despite the complexity, the program accounted for $45 billion in 2023, making it a critical pathway for businesses aiming to work with the federal government.
Scored Criteria: Evaluating Vendor Proposals
Once vendors meet the mandatory requirements, the evaluation moves to a more detailed review of proposal quality. For GSA contracts, the primary focus is on pricing. Federal buyers conduct a one-time negotiation to establish rates that are both fair and competitive. Striking the right balance – offering compliant pricing that aligns with federal standards while safeguarding profit margins – is a pivotal challenge. For businesses navigating this phase, GSA Focus provides expert negotiation support to help secure favorable terms.
How Federal Buyers Find and Invite Vendors
Finding Qualified Vendors
Federal buyers rely on SAM.gov to confirm a vendor’s Unique Entity ID (UEI) and ensure compliance with the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR). Being registered on SAM.gov is a non-negotiable step for any business seeking federal contracts.
But registration alone isn’t enough. Buyers dig deeper, evaluating vendors based on their past performance and compliance history. They examine Service Contract Reporting (SCR) data in SAM.gov to assess a vendor’s reliability and track record. Additionally, many agencies prioritize vendors with a GSA Multiple Award Schedule (MAS) contract. This contract not only signals a business’s credibility but also grants access to specialized platforms like GSA eBuy and GSA Advantage.
Here’s an eye-opening stat: While the GSA Schedule program managed $45 billion in 2023, only 4% of small businesses hold these contracts. This creates a unique dynamic – 44% of government awards receive just one bid, offering a less competitive landscape for businesses that qualify. These evaluations play a critical role when proposals are reviewed.
Posting Solicitations
Once federal buyers identify qualified vendors, the next step is to announce procurement opportunities. These opportunities are primarily posted on SAM.gov, the go-to platform for federal contracting notices. For vendors with GSA Schedule contracts, additional solicitations are shared through GSA eBuy and GSA Advantage, offering a streamlined bidding process for pre-approved businesses.
For vendors, keeping a close eye on SAM.gov is crucial to respond quickly to new opportunities. It’s equally important to ensure that all entity information is up-to-date. For those pursuing GSA contracts, the process can feel daunting. The paperwork and compliance requirements are often overwhelming, especially for newcomers. In fact, 57% of GSA Focus clients had no prior experience with government contracting before securing their first contracts, illustrating how professional guidance can simplify the journey.
How Federal Buyers Score and Review Bids
Scoring Bids Using Set Criteria
Federal buyers follow a well-defined evaluation process to score bids, particularly under FAR Part 15 for competitive negotiated acquisitions. The source selection authority (SSA) – often the contracting officer – puts together an evaluation team. This team includes experts in contracting, legal, logistics, and technical fields, who collectively assess proposals based on the criteria outlined in the solicitation. These criteria typically include technical excellence, past performance, management capability, personnel qualifications, and cost. The structured scoring process ensures that only proposals fully aligned with federal standards move forward.
Once the initial scoring is complete, the contracting officer identifies the highest-rated proposals and places them in a competitive range. Vendors in this range may have the opportunity to refine their offers, while those outside the range face elimination. For Lowest Price Technically Acceptable (LPTA) procurements, non-price factors are evaluated for basic acceptability, and any technical shortcomings lead to rejection. In Best Value (Trade-Off) procurements, higher-priced bids with superior technical scores can prevail if the added value justifies the cost.
| Common Bid Evaluation Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Technical Capability | Includes experience, expertise, past projects, equipment, and ability to meet specifications |
| Past Performance | Assesses integrity, reliability, and history of successful delivery |
| Price | Evaluates total cost, where the lowest price doesn’t always win |
| Compliance & Quality | Focuses on certifications, adherence to standards, and quality assurance processes |
| Delivery & Reliability | Examines timelines, history of on-time delivery, and ability to handle disruptions |
To increase your chances of making the competitive range, ensure your proposal aligns perfectly with the RFP criteria. Highlight verifiable past performance and use precise technical language. Strengths in management and risk mitigation can also make your bid stand out. Proposals that fail to meet these benchmarks are quickly eliminated, as explained below.
Why Bids Get Rejected
Proposals that don’t meet the scoring criteria are rejected for specific deficiencies. For example, bids are disqualified if they fail to meet responsibility standards – such as financial stability or performance capability – outlined under 48 C.F.R. §9.104-1, or if they fail to satisfy the requirements of the solicitation.
Common reasons for rejection include a lack of evidence demonstrating past performance, failure to meet the technical specifications outlined in the RFP, or submitting incomplete documentation, such as missing certifications. In LPTA procurements, any technical deficiency results in automatic rejection, even if the price is extremely competitive. Even minor deviations can cause disqualification.
To avoid rejection, review the solicitation documents thoroughly and ensure every scoring criterion is met. Confirm that your SAM.gov registration is up to date and that you meet all FAR responsibility standards. Double-check that all required certifications and technical specifications are addressed in full.
How Federal Buyers Select Vendors and Award Contracts
Selection Methods: Lowest Price vs. Best Value
Federal buyers typically rely on two main methods to select vendors: Lowest Price Technically Acceptable (LPTA) and Best Value Trade-Off. With the LPTA method, the focus is straightforward – award the contract to the lowest-priced vendor who meets all the technical requirements. This method works best for purchases that are simple and well-defined, like standardized IT hardware. Here, cost savings take priority, but quality standards must still be met. Non-price factors are reviewed only to confirm they meet the minimum technical thresholds, without ranking or scoring.
The Best Value Trade-Off approach, on the other hand, allows buyers to choose a higher-priced proposal if the additional benefits justify the higher cost. This method evaluates factors like technical expertise, past performance, management capability, and risk reduction alongside price. For instance, a vendor offering superior technical solutions may win a contract even at a 10–20% higher cost if their proposal reduces long-term risks. Federal guidelines require quality factors to be considered in every selection process, which has led to this method being increasingly favored in complex procurements.
When preparing a bid, it’s essential to align your strategy with the evaluation method. For LPTA, focus on competitive pricing that meets all technical requirements. For Best Value, emphasize your technical strengths, risk mitigation strategies, and provide solid supporting data. Pay close attention to the solicitation details, as evaluation criteria can vary. For example, technical factors might weigh 60% of the total score, past performance 30%, and price only 10% in some cases. Once the top proposals are identified, the process moves into the negotiation phase and final contract awards.
Negotiation and Contract Award
Once proposals are narrowed down, the contracting officer enters negotiations with selected vendors to address any remaining questions, clarify details, and finalize terms. This phase often involves detailed discussions about pricing and performance to ensure everything aligns with the government’s requirements. In GSA Schedule contracts, these negotiations typically revolve around pricing and regulatory compliance, with the goal being to secure the best overall value – not necessarily the lowest price.
After negotiations wrap up, the Source Selection Authority makes the final decision based on documented evaluations and trade-off analyses. The contracting officer then notifies the winning vendor and offers debriefings to those who were not selected. Before a contract is officially awarded, the government ensures the chosen vendor meets all responsibility standards outlined in FAR 9.104, including financial stability and performance capability. It’s also crucial to keep your SAM.gov registration up to date during this process.
The final contract will specify all terms, including deliverables and payment schedules (often net 30 days). For vendors navigating GSA Schedule contracts, experts like GSA Focus can provide valuable support in negotiating fair and compliant terms.
Meeting GSA Schedule Requirements
Past Performance and Compliance Requirements
When federal buyers evaluate your proposal, they want proof that you can deliver. They’ll look at verified past performance on contracts – whether federal, state, local, or commercial – that align with the scope of your proposal. If you’ve worked on federal contracts before, your CPARS (Contractor Performance Assessment Reporting System) ratings will be a key factor. These ratings assess critical areas like quality, adherence to schedules, cost management, and business relationships. High CPARS scores demonstrate reliability and lower the risk of performance issues.
For small businesses, presenting commercial contracts that closely reflect the work expected under federal contracts can level the playing field. Highlight your track record of on-time delivery, customer satisfaction, and effective project management to show you’re a dependable choice.
Compliance is just as important. Your products or services must meet Trade Agreements Act (TAA) requirements, meaning they should be manufactured or substantially transformed in designated countries. Additionally, adhering to GSA-specific rules – such as submitting quarterly sales reports, paying the 0.75% Industrial Funding Fee (IFF), and keeping your GSA Advantage! catalog updated – is essential to maintain compliance.
Once you’ve established a strong performance history and a solid compliance framework, the next step is developing pricing that aligns with federal expectations.
Pricing Strategies for GSA Contracts
After performance and compliance, pricing becomes the deciding factor. To stay competitive, GSA pricing needs to strike a balance between market rates and profitability. Start by using your commercial price list to determine your best pricing for your Most Favored Customer (MFC). Federal buyers expect prices to be fair and reasonable, which means they’ll compare your rates to those of other Schedule holders in the same Special Item Number (SIN) and to benchmarks in the commercial market.
Consider offering volume or term discounts for larger contracts or longer durations, but make sure to maintain a sustainable minimum price. Don’t forget to include the 0.75% IFF in your pricing margins. Tools provided by GSA, along with public award data, can help you analyze competitor rates and position your pricing effectively.
Transparency is key when it comes to pricing. By using the Commercial Sales Practices (CSP) format, you allow GSA to verify your standard discounts and terms, ensuring your pricing remains competitive and compliant. A clear and repeatable pricing policy not only simplifies audits but also makes future contract modifications easier. If you’re new to the GSA Schedule process, working with experts like GSA Focus can help you craft a pricing strategy that meets federal standards while protecting your margins.
Conclusion
Federal buyers evaluate vendors based on a structured process outlined by FAR, focusing on mandatory requirements, technical capability, past performance, and pricing. To succeed in this space, aligning your approach with these criteria is essential.
Start by ensuring your SAM.gov registration is complete and up-to-date. Gather documentation that highlights your past performance and demonstrates your ability to meet solicitation requirements. Tailor your proposals to align closely with the criteria outlined in solicitations, and establish systems that showcase your reliability and compliance.
Once compliance is in place, shift your attention to competitive pricing. Transparency is key – both in pricing and compliance. For GSA Schedule contracts, aim to offer rates that are commercially competitive while meeting federal standards. The GSA Schedule streamlines the buying process for federal agencies, offering them access to pre-vetted vendors with pre-negotiated terms. If you’re a small business entering this space for the first time, partnering with specialists like GSA Focus can help manage the complexities of document preparation, compliance, and negotiations, making the process less daunting.
To further minimize risk, provide clear, thorough documentation and demonstrate a strong track record of delivering projects on time and within budget. These steps not only build trust but also align your business with the structured criteria federal buyers rely on to select vendors.
Success in federal contracting comes down to preparation, compliance, and a deep understanding of how the government evaluates and selects vendors. The more you align your operations and proposals with these expectations, the better positioned you’ll be to win contracts consistently.
FAQs
Why is registering on SAM.gov important for federal contractors?
Registering on SAM.gov is an essential move for any business aiming to work with the federal government. This registration process assigns your business a unique entity ID, which is a must-have for bidding on federal contracts, exploring opportunities, and receiving payments.
Without completing this registration, your business won’t be eligible for federal contracting opportunities or able to meet government compliance standards. It’s a way to verify and confirm that your business is qualified to engage in federal procurement activities.
How do federal buyers assess a vendor’s past performance?
When federal buyers evaluate vendors, they focus heavily on past performance. They look at how well a company has handled previous contracts, paying close attention to factors like meeting delivery deadlines, the quality of the work delivered, and compliance with regulations. Performance ratings and references also play a significant role in assessing a vendor’s reliability and consistency.
A solid history of strong performance can go a long way in building trust with federal buyers, significantly boosting a business’s chances of securing future contracts.
What advantages come with having a GSA Schedule contract?
Having a GSA Schedule contract can be a game-changer for businesses looking to tap into the lucrative federal marketplace. With access to over $50 billion in annual federal spending, this contract provides a reliable revenue stream backed by government funding. It also simplifies the procurement process, cutting down on competition and significantly shortening sales cycles.
Another advantage is the ability to negotiate pricing upfront, ensuring fair rates that support long-term financial stability. This predictability can be especially valuable when planning for the future. Plus, holding a GSA Schedule contract positions your business as a trusted partner for federal buyers, creating consistent opportunities – even when the economy faces challenges.
Related Blog Posts
- Ultimate Guide to Federal Buyer Relationships
- Types of Federal Procurement Methods Explained
- How GSA Evaluates Bid Opportunities
- Federal Procurement Process Overview



