Uploading your product catalog to GSA Advantage is a mandatory step to maintain compliance with federal contracting rules and unlock access to government sales opportunities. Here’s what you need to know:
- Deadlines: Submit your catalog within 30 to 180 days of contract award to avoid penalties.
- Importance: Without a live catalog, you can’t access tools like eBuy, missing out on federal bidding opportunities.
- Steps: Confirm your GSA Schedule Contract status, ensure your approved pricelist is accurate, and gather all required product details (e.g., manufacturer name, part numbers, TAA compliance).
- Upload Options: Use SIP for smaller catalogs or EDI for larger inventories. Starting September 2025, the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP) is mandatory for new contracts.
- Post-Upload: Verify your catalog’s publication, update it regularly, and ensure compliance with GSA requirements.
To avoid errors, double-check data formatting, follow GSA guidelines, and choose the right upload method for your needs. A well-maintained catalog ensures visibility and access to federal buyers, helping you maximize sales opportunities.
Before You Upload
Confirm Your GSA Schedule Contract Status
Start by registering your contract on the Vendor Support Center (VSC) using your contract number and Unique Entity Identifier (UEI). This step is non-negotiable – registering on the VSC ensures you avoid errors in the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP) and gain access to eBuy. Keep in mind, only those listed as Authorized Negotiators on your contract are allowed to register on the VSC and manage the FCP.
"If you do not register [with the VSC] first, you will encounter errors in FCP, and you will not be able to login to eBuy." – GSA Vendor Support Center
Make sure your SAM.gov registration is active and updated annually; this is essential to keep your contract valid. Double-check your company’s contact details and awarded Special Item Numbers (SINs) on GSA eLibrary, as Contracting Officers and buyers rely on this information to find your business. Additionally, ensure all Authorized Negotiators have an active FAS ID to access the FAS Catalog Platform.
Once your contract status is squared away, confirm that your approved pricelist aligns with your contract terms.
Check Your Approved Pricelist
After confirming your contract status, verify that your catalog matches your approved pricelist. Only include products, services, and solutions that have been awarded on your contract. Everything should align with your Final Proposal Revision (FPR) – this includes SINs, pricing, and terms outlined in Clause I-FSS-600. Review your award documents to ensure details like minimum order requirements and points of contact match your contract.
"Your GSA Advantage posting should mirror your approved GSA price list at all times. This means only pricing, products, and services approved by your Contracting Officer through the award/modification process can be posted on Advantage." – Federal Schedules, Inc.
Before uploading, clean up your data. Remove special characters like "Before uploading, clean up your data. Remove special characters like "$" and "%", convert percentages into decimals (e.g., 0.05 instead of 5%), and keep manufacturer part numbers under 40 characters to avoid system errors [2]. If you need to update a manufacturer name or part number after submission, use the "Delete and Add" function in FCP instead of making direct changes [2].quot; and "%", convert percentages into decimals (e.g., 0.05 instead of 5%), and keep manufacturer part numbers under 40 characters to avoid system errors. If you need to update a manufacturer name or part number after submission, use the "Delete and Add" function in FCP instead of making direct changes.
Collect Product Information
For each product, gather the contract number, manufacturer name, and manufacturer part number. You’ll also need the following details:
- Manufacturer’s part number and name
- A brief description (commodity name)
- Country of origin for Trade Agreements Act (TAA) compliance
- Associated SIN
If your SIN requires it, include Universal Product Codes (UPCs).
Prepare product images in JPG or GIF format. The item should take up at least 80% of the image area, with a resolution of at least 500×500 pixels – though GSA recommends 800×800 pixels for better clarity. Keep file sizes under 1MB, limit filenames to 80 characters, and use only letters, numbers, and underscores. Organize all images into a ZIP file for easy upload.
You’ll need three key file types for submission:
- A Product File listing all approved products and services.
- A Terms and Conditions (T&C) File in PDF, DOC, XLS, or HTM format. If using a separate Product File, exclude pricing from the T&C File.
- A Services Plus File for offerings not directly orderable on GSA Advantage.
Be sure to include FOB terms and lead times (delivery days) at the contract level. Use the SIN-MOL-Photo-UPC Table provided by GSA to determine if your SIN requires specific photos or UPCs.
Adding Products in FCP – MAS Vendor Training
Select Your Upload Method
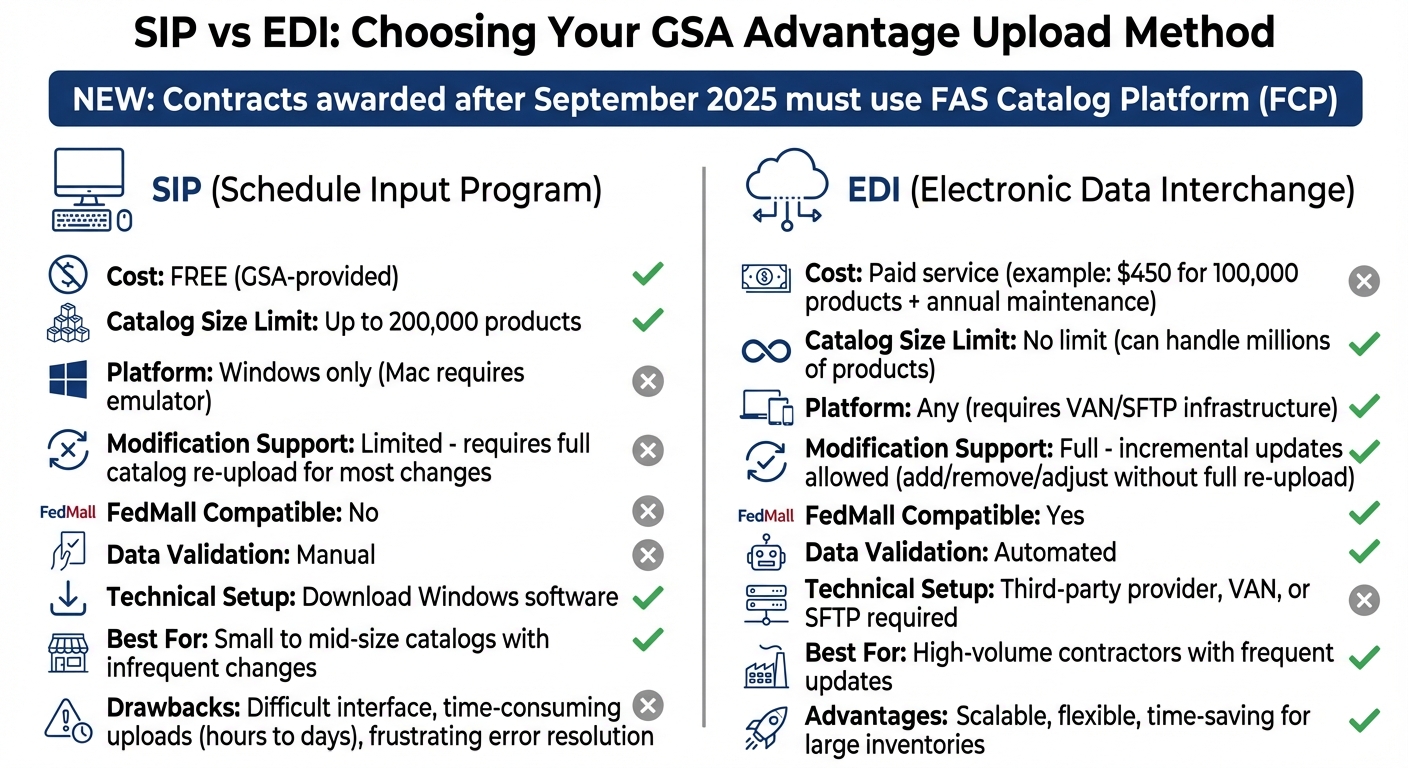
GSA Advantage Upload Methods: SIP vs EDI Comparison
When deciding how to upload your catalog, consider the size of your inventory and how often updates are needed. You have two main options: Schedule Input Program (SIP) or Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). SIP is better suited for smaller, less dynamic catalogs, while EDI is ideal for larger inventories that require frequent updates.
Important note: Contracts awarded after September 2025 must use the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP) instead of SIP or EDI. The following guidance applies only to current GSA contractors and new VA contractors already using SIP or EDI.
Schedule Input Program (SIP)
SIP is a free Windows-based tool provided by GSA for catalog uploads. It’s designed for catalogs with up to 200,000 products. However, if you use a Mac, you’ll need a Windows emulator to run the software.
The program supports data imports from standard ASCII text files, DBF files (version 3.0 or higher), and MS Excel files (MS Office 97 or newer). While SIP is free, it has some drawbacks: the interface is difficult to navigate, error resolution can be frustrating, and uploading large catalogs may take hours – or even days. Another challenge is that most updates require re-uploading the entire catalog, as SIP doesn’t allow for quick changes like adding or removing individual products.
"SIP is definitely faster than the previous method of uploading your catalog – much the same way as cycling is faster than walking – but it also introduces several new obstacles that can often frustrate even the most hardened of wills." – Price Reporter
One critical step: you must process the Contracting Officer’s response file before making any additional uploads. This requirement can delay updates, which is a concern in fast-changing markets.
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
EDI offers a more efficient and scalable solution, especially for larger inventories. It uses a computer-to-computer system to exchange business documents in standardized formats, specifically Transaction Set 832 for catalogs. Unlike SIP, EDI doesn’t have size limitations and can handle millions of products. For example, Sensoft, a leading EDI provider, has uploaded nearly half of all products on GSA Advantage.
One of EDI’s biggest strengths is its flexibility. You can make incremental updates – such as adding new items, removing discontinued ones, or adjusting prices – without re-uploading your entire catalog. This is a major time-saver for businesses with large or frequently changing inventories.
However, EDI requires additional resources. You’ll need a third-party service provider, a Value Added Network (VAN), or a Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) setup. Costs vary by provider; for instance, one charges $450 for an initial upload of 100,000 products, plus an annual maintenance fee. Some providers, like Price Reporter, even offer free initial uploads for up to 100,000 products.
"Anything SIP can do EDI can do better, so why cycle when you can drive?" – Price Reporter
If your catalog is large or requires frequent updates, EDI can save you significant time and effort over the course of your contract.
SIP Upload Checklist
Install SIP Software
Begin by downloading and installing the SIP software from the Vendor Support Center (VSC). This software is provided by GSA at no cost, but you’ll need administrator rights on your computer to complete the installation. If you lack these permissions, reach out to your IT department for assistance. Keep in mind, SIP is compatible only with Microsoft Windows, so Mac users will need to rely on a Windows emulator to run the program.
Once installed, the software includes an Import Program that simplifies adding catalog data. You can import data directly from MS Excel (version 97 or newer), DBF files (version 3.0 or higher), or standard ASCII text files, saving you from manual data entry. Need help? Press F1 at any time within the software for guidance.
Check Product Data for Errors
Carefully review your product data before proceeding. GSA identifies each product by combining your contract number, manufacturer part number, and manufacturer name. Double-check that these details are accurate and unique to avoid duplication. Additionally, ensure part numbers don’t exceed the 40-character limit – longer part numbers will result in automatic errors.
If your catalog includes product photos, the filenames in your data must exactly match the photo file names in your ZIP archive. Errors here can delay your upload. Once everything checks out, you’re ready to move forward.
Upload Your Catalog
After confirming your data is error-free, open SIP and navigate to Communications → "Create Catalog Files". This step backs up your data and generates the required FSS Terms and Conditions Price List. Once the files are created, you can proceed with uploading your catalog.
Remember to upload your electronic catalog within 30 days of your contract award. After submission, GSA will review your catalog and send you a Response File. You’ll need to retrieve and process this file in SIP before making any further updates. If your catalog is rejected, you have 30 calendar days to resolve the issues and resubmit. This process ensures your local software stays aligned with the GSA Advantage database.
After Upload: Verification and Updates
After uploading your catalog, it’s crucial to verify its publication and keep your product information up-to-date. This ensures your offerings remain compliant and attractive to federal buyers.
Verify Publication
To confirm your catalog is live, head over to GSA Advantage and search using your contract number, vendor name, or relevant product keywords. Regularly check that your products, images, and descriptions appear as expected.
The verification process varies depending on your upload method:
- FCP Users: Your catalog is published automatically once the "Baseline" modification is approved in eMod.
- SIP Users: You’ll receive a Response File indicating whether your submission was approved or rejected.
- EDI Users: You’ll typically get an email notification once your catalog is approved by the Contracting Officer (CO).
Additionally, check GSA eLibrary to verify that your awarded pricelist (text file) is visible alongside your GSA Advantage product upload. If you can log in to GSA eBuy and respond to RFQs, that’s another sign your catalog has been approved and published.
"The completeness and accuracy of the data submitted is your responsibility. Please ensure that your products and services are adequately described and remain current." – GSA
If your catalog is rejected, address the issues promptly to avoid delays in making your products available to federal buyers.
Once your catalog is live, maintaining its accuracy and relevance becomes an ongoing task.
Manage Product Changes
Keeping your catalog updated is essential. Any changes – whether they involve pricing, descriptions, or product listings – must first be submitted as a contract modification through the eMod system. Once approved, you generally have 30 days to update your catalog on both GSA Advantage and eLibrary.
For those using SIP, ensure you process the response file from your previous submission before sending new updates to maintain system synchronization. EDI users should monitor the 824 transaction set, which flags specific data errors if your catalog file is rejected.
"Once your catalog data is online, you should check it frequently to make sure it appears as you had intended. If not, open up a subsequent modification/FCP action to make the applicable changes." – Vendor Support Center
Need to lower prices quickly? Use the Temporary Price Reduction (TPR) feature. These changes take effect as soon as you submit the modification via eMod. Also, ensure your Order Status Point of Contact is up-to-date in the PO Portal to stay on top of purchase orders.
Staying proactive with updates keeps your catalog accurate and ensures you’re ready to meet the needs of federal buyers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using a detailed checklist can help you sidestep common errors and maintain a compliant, efficient catalog. Being mindful of these frequent pitfalls can save you a lot of time and unnecessary stress.
Meet GSA Compliance Requirements
Ensuring Trade Agreements Act (TAA) compliance is non-negotiable. Every product you list must align with TAA requirements. Uploading non-compliant products could lead to rejection or even contract complications.
Here are some common compliance mistakes to watch out for:
- Formatting errors: For example, using special characters in numeric fields or entering percentages as whole numbers instead of decimals (e.g., 0.75 instead of 75%).
- Product identification issues: Each product must have a unique manufacturer part number and name. Keep part numbers under 40 characters.
- Missing documentation: Failing to upload your required Terms and Conditions (T&C) Price List to the GSA eLibrary within the specified timeframe can cause major issues.
"If your terms and conditions are not uploaded, you are not in compliance and your contract will be removed." – ColeyGSA
Other errors include uploading products under Special Item Numbers (SINs) that aren’t part of your awarded contract. For those using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) uploads, forgetting to include Free on Board (FOB) terms or lead time details at the contract level can lead to rejections. If you’re enrolled in Transactional Data Reporting (TDR), remember that Most Favored Customer (MFC) information isn’t required.
Lastly, selecting the wrong upload method can lead to technical headaches, so it’s essential to choose wisely.
Pick the Right Upload Method
Choosing the correct upload method can make compliance easier and reduce errors. Starting in September 2025, the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP) will be mandatory for all newly awarded contracts. If your contract falls under this category, FCP is your only option.
For existing contracts, it’s important to understand the distinctions between the Schedule Input Program (SIP) and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI):
| Feature | SIP | EDI |
|---|---|---|
| Catalog Size Limit | Up to 200,000 products | No size limit |
| Modification Support | Limited | Full support |
| FedMall Compatibility | No | Yes |
| Data Validation | Manual | Automated |
| Technical Setup | Windows software required | Requires VAN/SFTP infrastructure |
| Best For | Small to mid-size catalogs with infrequent changes | High-volume contractors with frequent updates |
SIP comes with its own set of challenges. It only works on Windows, so Mac users will need an emulator to run it. On the other hand, EDI offers greater flexibility but requires more technical expertise. You’ll need to handle 832 transaction sets and maintain either a Value Added Network (VAN) or SFTP connection. This method is best suited for contractors with robust IT support and frequent catalog updates.
Conclusion
Uploading your GSA Advantage catalog involves careful planning, strict adherence to guidelines, and consistent upkeep. Start by confirming your contract status, gathering detailed product information, and registering with the GSA Vendor Support Center to obtain your FAS ID. Remember, your catalog file must be submitted within 30 days of contract award, and your Terms and Conditions Price List must be uploaded to both GSA Advantage and eLibrary to stay compliant.
Choose the upload method that aligns with your inventory size and how often you’ll need to update it. Starting September 2025, all new contracts will require the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP). For existing contracts, compare the limitations of SIP with the technical demands of EDI to decide which works best for your catalog’s scope and frequency of updates. With federal buyers spending over $1 billion annually on GSA Advantage, ensuring your products are accurately listed and easy to find is crucial.
Once uploaded, verify that your catalog is displayed correctly and reflects any contract changes promptly. Update your catalog within 30 days of modifications to maintain compliance. Additionally, provide order status updates using the PO Portal, EDI, or cXML. Staying on top of updates is key to keeping your catalog competitive. Don’t forget your ongoing responsibilities, including quarterly (or monthly for TDR contracts) sales reporting, paying the 0.75% Industrial Funding Fee, and renewing your SAM.gov registration every year.
For small businesses, navigating GSA’s technical and compliance requirements can feel overwhelming. If SIP software, EDI transactions, or compliance rules are proving to be a challenge, professional help can make all the difference. GSA Focus offers full-service support tailored to small businesses, covering everything from document preparation to compliance management. This allows you to concentrate on serving federal customers instead of grappling with technical hurdles.
A properly managed GSA Advantage catalog not only ensures compliance but also positions your business for success in the federal marketplace. By following these steps, you can unlock new opportunities and establish a strong presence in government contracting.
FAQs
What’s the difference between SIP and EDI for uploading GSA catalogs?
When it comes to submitting product catalogs to GSA Advantage, two main options stand out: SIP (Schedules Input Program) and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange). While both accomplish the same task, they differ in how they work, their user-friendliness, and their ability to handle large-scale operations.
SIP is a free tool provided by GSA, making it a popular choice for contractors looking to avoid licensing fees. But, there’s a catch – its interface can be tricky to navigate, and the process of validating data can eat up a lot of time. Plus, if your catalog includes more than 200,000 items, SIP starts to struggle. Even uploads can take hours or, in some cases, days to complete.
EDI, meanwhile, is the more advanced option. It often requires either third-party assistance or integration into your existing systems, which can mean additional expenses. However, it makes up for that with faster uploads, automated error checks, and the ability to handle massive catalogs without breaking a sweat. For businesses managing extensive product lists, EDI is typically the more efficient and reliable choice.
What steps should I take to ensure my product data complies with GSA requirements?
To meet GSA requirements, start by registering with the GSA Vendor Support Center and uploading your product catalog via the FAS Catalog Platform or SIP. Your catalog must adhere to GSA guidelines, including compliance with clauses 552.238-88 and I-FSS-600. Use standardized fields such as MPN, UPC-A, and provide clear, detailed product descriptions. Additionally, make sure your pricing falls within GSA-approved ranges.
Once uploaded, carefully review the system-generated compliance and pricing reports. Address any flagged issues promptly before submitting your catalog. This step is essential to prevent delays and ensure your catalog meets all required standards.
What should I do if my GSA Advantage catalog upload is rejected?
If your GSA Advantage catalog upload gets rejected, the first step is to carefully examine the rejection notice. This notice will pinpoint the reasons for rejection, which could include missing required fields, pricing mismatches, or formatting errors. Compare the feedback with your catalog to identify exactly what needs fixing.
To catch and address errors, use tools like the Schedule Input Program (SIP) or the FAS Catalog Platform (FCP). These platforms can help you spot issues with formatting, missing fields, or compliance requirements. Make the necessary updates – this might include refining product descriptions, ensuring your pricing aligns with contract terms, or switching to the latest templates. Don’t forget to reattach any required documents or images if they were missing.
Once you’ve resolved the issues, re-submit your catalog through the appropriate platform. If you’re still running into problems or if the rejection notice isn’t clear, reach out to the GSA Vendor Support Center for guidance. You can also consider working with GSA Focus, a service that specializes in helping vendors navigate GSA Schedule requirements, ensuring your submission meets all standards.
Related Blog Posts
- GSA Post-Award Checklist for Contractors
- Checklist for GSA Construction Contract Compliance
- How to Get Found on the GSA Advantage Website
- GSA Advantage Website 101: A Small Business Guide


